 |
Image Component Library (ICL)
|
 |
Image Component Library (ICL)
|
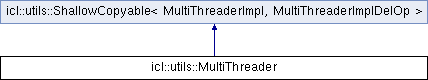
Utility class for parallelizing algorithms. More...
#include <MultiThreader.h>
Classes | |
| class | Work |
| plugin class for work packages performed parallel More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef std::vector< Work * > | WorkSet |
| set of work packages, that should be performed parallel More... | |
 Public Types inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > Public Types inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > | |
| typedef ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > | ParentSC |
Public Member Functions | |
| MultiThreader () | |
| Empty (null) constructor. More... | |
| MultiThreader (int nThreads) | |
| Default constructor with defined set of working threads. More... | |
| void | operator() (WorkSet &ws) |
| applying operator (performs each Work* element of ws parallel) More... | |
| int | getNumThreads () const |
| returns the number of WorkThreads More... | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > Public Member Functions inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > | |
| bool | isNull () const |
| returns wheter the objects implementation holds a null pointer More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > Protected Member Functions inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > | |
| ShallowCopyable (MultiThreaderImpl *t=0) | |
| create a the implementation with a given T* value More... | |
 Protected Attributes inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > Protected Attributes inherited from icl::utils::ShallowCopyable< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > | |
| SmartPtrBase< MultiThreaderImpl, MultiThreaderImplDelOp > | impl |
| shared pointer for the classes implementation More... | |
Utility class for parallelizing algorithms.
The Multithreader class provides a simple interface to parallelize algorithms. To achieve a multi-threaded implementation of an algorithm, you have to split the computation loop into N parts (Work-Packages or short Work). Each of this Works will be computed in a single thread internally when given to the apply operator of the MultiThreader.
Please note This tool was written before openmp became popular and part of compilers. Today we recommend to use openmp rather then the Multithreader class.
The following example explains how to parallelize a simple function-call
The following benchmark results were obtained:
However, the MultiThreader provides a powerful interface for parallelizing code, it is still a bit inconvenient to use. The Example above has shown, that the programmer has to write about 10 additional line for the function wrapper and another 4 lines to create the WorkSet and to fill the MultiThreader instance with it.
For more convenience some additional high level classes and functions should be implemented. For instance the SplittedUnaryop class of the ICLFilter package, which provides a top level interface for parallelizing unary operators (class interface UnaryOp)
| typedef std::vector<Work*> icl::utils::MultiThreader::WorkSet |
set of work packages, that should be performed parallel
| icl::utils::MultiThreader::MultiThreader | ( | ) |
Empty (null) constructor.
| icl::utils::MultiThreader::MultiThreader | ( | int | nThreads | ) |
Default constructor with defined set of working threads.
| int icl::utils::MultiThreader::getNumThreads | ( | ) | const |
returns the number of WorkThreads
| void icl::utils::MultiThreader::operator() | ( | WorkSet & | ws | ) |
applying operator (performs each Work* element of ws parallel)
 1.8.15
1.8.15